Case History:
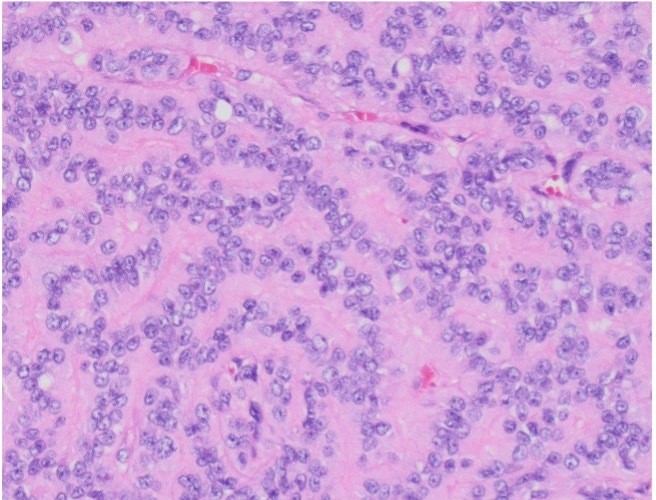
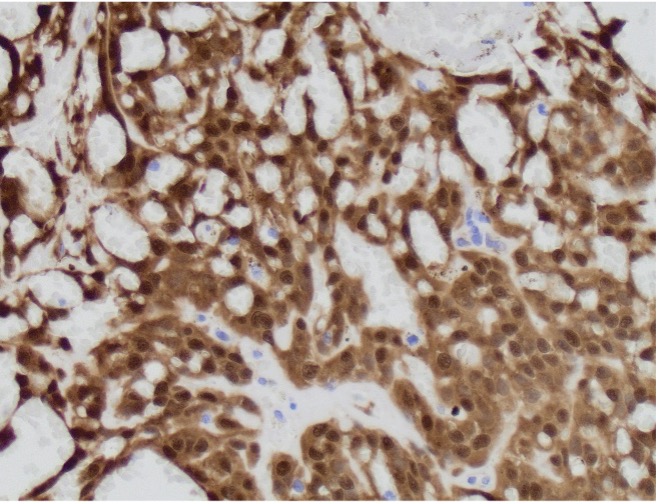
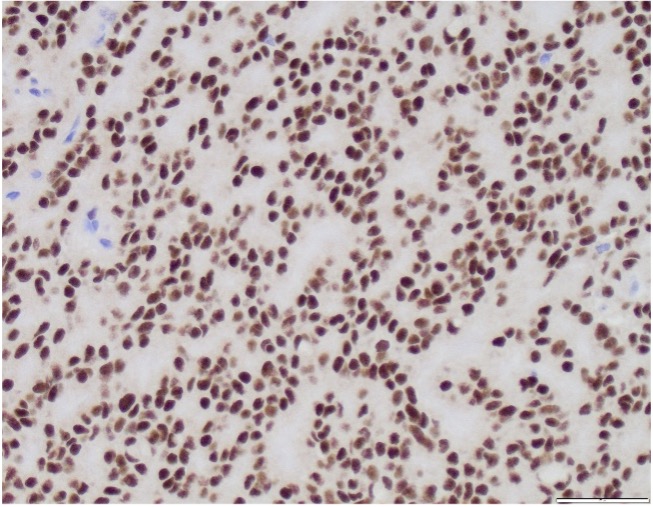
A 64 year-old man with history of clear cell renal cell carcinoma s/p nephrectomy (2021) presents with scrotal pain and firmness. Ultrasound reveals a 2 cm solid lesion. Serum tumor markers (hCG and AFP) were normal. The tumor was negative for SALL4, OCT3/4, AFP, and showed focal patchy positivity for pancytokeratin (focal). PAX8 was weakly positive. Additional stains are displayed in the pictures.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma.
B. Sertoli cell nodule.
C. Neuroendocrine tumor.
D. Seminoma.
E. Sertoli cell tumor.
Correct Answer: E. Sertoli cell tumor.
Discussion:
Sertoli cell tumors account for < 1% of all testicular neoplasms. Sertoli cell tumors are usually well-circumscribed, firm, lobulated, tan-white with occasional cystic changes and hemorrhage. Microscopically they show tubular differentiation in the form of solid or hollow tubules. However, the appearance can be very variable: diffuse growth, solid nests, trabeculae and cords. Many tumors show areas of sclerotic stroma. Most Sertoli cell tumors have round nuclei with small nucleoli and a few mitotic figures. Their cytoplasm can be very variable, from vacuolated to signet ring-like and abundant eosinophilic. By immunohistochemistry, the most helpful markers are SF-1 and beta-catenin (due to CTNNB1 mutation). Inhibin and calretinin can also be helpful, however, less frequently expressed.
Sertoli cell tumor must be differentiated from Sertoli cell nodules. The latter are usually microscopic and measure few millimeters.
Sertoli cell tumors can be potentially misdiagnosed as seminoma when the predominant pattern is solid. The lack of lymphocytic infiltrate and germ cell neoplasia in situ, coupled with the contrasting negativity for SALL4, OCT3/4 and PLAP and reactivity for SF-1 can help in the diagnosis.
Chromogranin and synaptophysin has been also reported in Sertoli cell tumor and therefore, neuroendocrine tumors (NET) enters the differential diagnosis. The presence of characteristic chromatin pattern of NET, frequent association with a teratomatous component, and negativity for SF-1 will support NET.
Lastly, given that a subset of Sertoli tumors can be reactive with PAX8, like in this case, metastatic renal cell carcinoma can be considered. Strong positivity for SF1 argues against this diagnosis.
References:
WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Urinary and male genital tumours. Lyon (France): International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2022. (WHO classification of tumours series, 5th ed.; vol. 8). https://publications.iarc.fr/610.
Mesa H, Zhang C, Manivel JC, Ulbright TM. Immunophenotypic comparison of testicular sclerosing Sertoli cell tumors and Sertoli cell tumors not otherwise specified. Hum Pathol. 2017 Oct;68:99-102. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2017.08.022. Epub 2017 Sep 2. PMID: 28873352.
Ulbright, T. M., et al. (2022). Tumors and Tumor-Like Lesions of the Testis and Adjacent Tissues, American Registry of Pathology. https://doi.org/10.55418/9781933477220
Case contributed by Valeria L. Dal Zotto, M.D., Assistant Professor, Women's Health