Case History:
A female patient with cystic fibrosis in her mid-twenties has a positive AFB sputum culture. Below is a Kinyoun stain of positive MGIT tube fluid.
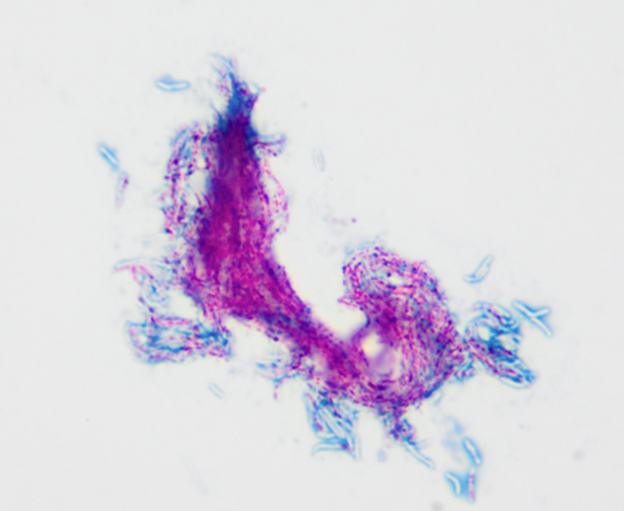
What is most likely etiology of infection?
A. M. Tuberculosis
B. N. Farcinica
C. M. Abscessus
D. M. Gordonae
Correct Answer: C. M. Abscessus
Discussion:
The images show branching, beaded bacterial rods that have taken up carbol fuchsin stain indicative of the genus Mycobacterium. There is slight cording which can be found in all mycobacterium but is indicative of increased virulence.
CF patients are at increased risk of pulmonary infection with multi-drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Burkholderia cepacia complex, and non-tuberculosis mycobacteria (NTM). A positive AFB culture from sputum from a CF patient is at low risk for MTB infection unless there is travel history or known contact with someone with an acute pulmonary TB infection. Therefore A) is incorrect.
Nocardia spp is more relevant to transplant patients that are intensely immunosuppressed and often also associated with neurological symptoms. Additionally, Nocardia spp is Kinyoun stain negative. B) is incorrect.
Mycobacterium gordonae is almost always considered a contaminant. It is colloquially called “tap-water bacillus” for its ubiquity in the environment. C) is incorrect.
MAC and M. abscessus are the most common cause of pulmonary AFB infections in CF patients. Therefore, C) is the answer. M. abscessus is a rapidly-growing mycobacterium that can be multi-drug resistant. It is split into 3 subspecies: abscessus, bolletii, and massiliense, with M. abscessus subspecies abscessus being the most isolated in the USA. Approximately 80% of this subspecies are resistant to macrolides, a key component of NTM multi-drug antibiotic regimen. Therefore, M. abscessus is regarded as one of the most challenging AFB infections to treat.
Case contributed by: Filipe Cerqueira, Ph.D., Assistant Professor, Laboratory Medicine