Research & Innovation
This study was done in mice and with a novel, tissue-engineered, three-dimensional breast cancer mimetic system.
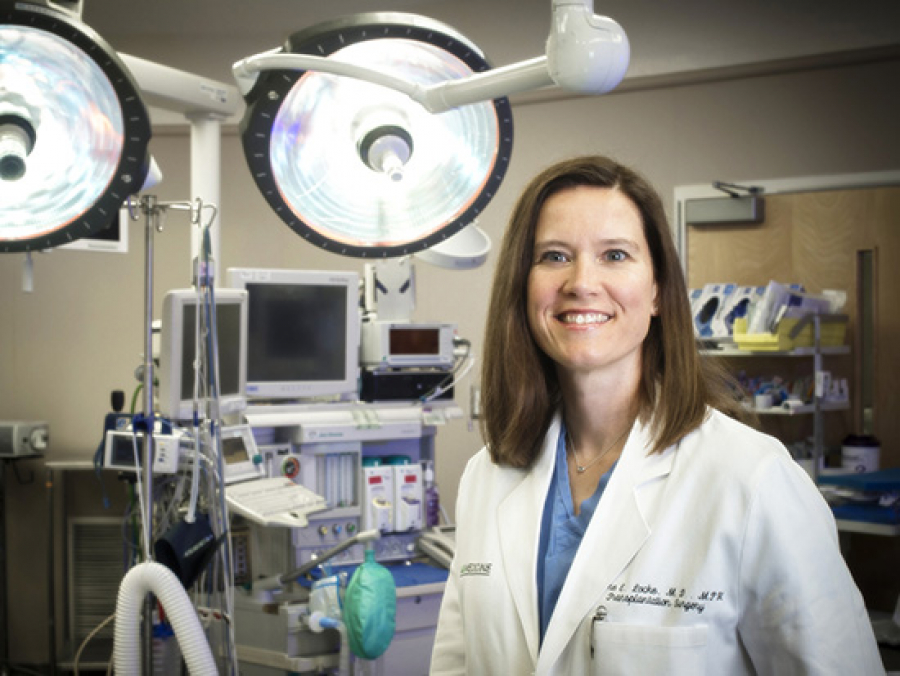
New evidence for sex disparity in liver transplants suggests a change may be needed in how livers are allocated.
A mouse model and previous studies suggest that genetic intervention in SHANK3-related ASD may be most effective earlier in development.
This discovery may have clinical importance in management of heart failure.
A study conducted by UAB investigators has outlined the importance of strict blood pressure control in the development of atrial fibrillation, which can lead to poor outcomes such as stroke, heart attacks and death.
Gender identity and genetic sex are distinctly variable when it comes to pain tolerance, according to a study published in the Journal of Pain Research.
The study observed two diet types to test their impact on adolescents with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Students are examining 60 variables, including sidewalk conditions, crosswalks, blighted properties and advertisements in four Birmingham communities.
Coronary microvascular dysfunction is a precursor to later heart disease, heart failure and possible death.
UAB orthopaedic surgeons report that the cost of orthobiologics, promising but not fully proven therapies, can vary widely across the nation.
Study points to a potential immediate treatment for this devastating disease.
Scientists are racing to determine which genealogy most accurately represents the evolutionary history of sea turtles — a challenging proposition.
Five-year, research-funding growth has grown by more than $154 million, marking a 34.4 percent increase in grants and awards won by faculty.
This study included preclinical experiments and use of bronchoalveolar cells from IPF patients.
This first-of-its-kind study aims to address this information gap by examining total net worth in conjunction with five components of wealth.
A new study blunts hopes that metformin might help exercising seniors gain more muscle mass.
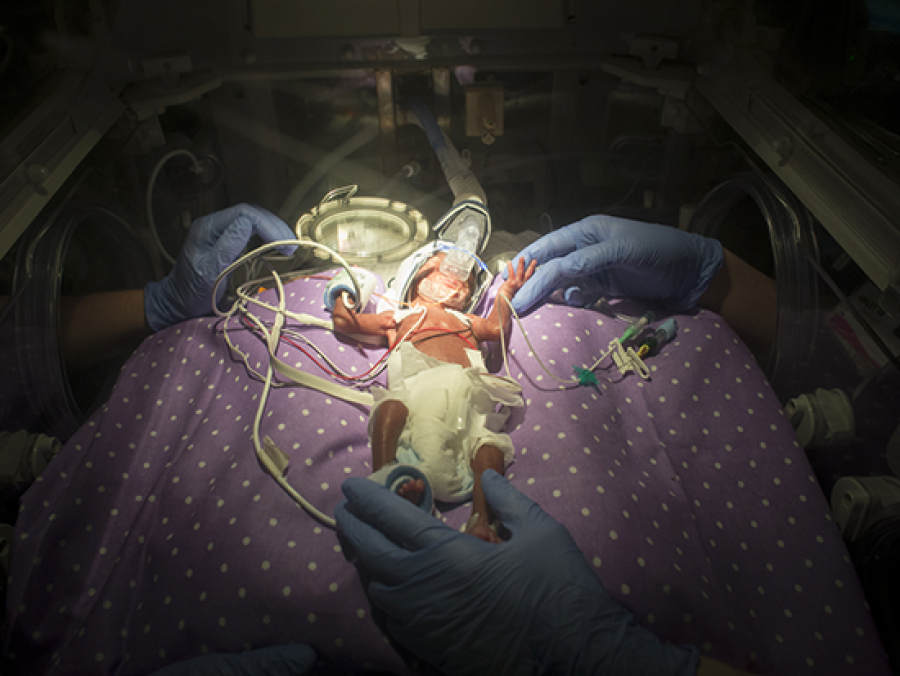
Excess exposure to oxygen can cause long-term effects on preterm infants.
IgA nephropathy is the leading primary glomerulonephritis worldwide.
A team of UAB researchers found even a small influence from AAT dogs is meaningful and valuable to someone after a life-changing spinal cord injury.
UAB researchers have found a previously unknown gene variant that appears to contribute to movement disorders.
Historically, Americans have chosen conflict avoidance over violence in property rights.
Research shows that young children are at a particular risk for pedestrian injuries in parking lots, and interventions should be made to decrease this risk.
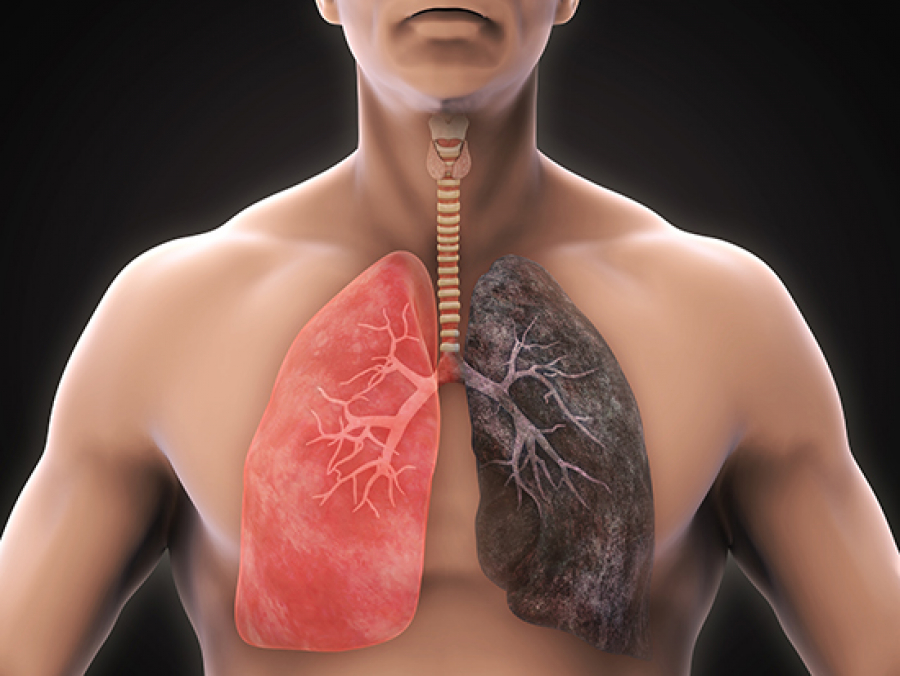
Airway fractal dimension gives added prognostic information over traditional CT scan measures in COPD.
Sensory processing difficulties, which affect one in six people, can make public spaces a nightmare and lead to traumatic meltdowns. A UAB expert teaches venues around the world how to help rather than hurt. Here’s her advice.
The International Symbol of Access has been criticized for its inadequate representation of disability diversity, poorly representing universal design of space and products.
A new discipline sits at the intersection of neuroscience and engineering, where lessons learned from circuits, networks and chips are combined with the latest findings on brain circuitry.
UAB professors publish distinct conceptual framework for entrepreneurship in educational settings.
A new screening tool developed at UAB has been shown to be an effective aid in determining the severity of cognitive issues.
Groundbreaking research from UAB shows that out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is the third leading cause of years lost and years lived with a disability due to a disease.
Attention, reasoning and memory could be improved with resistance exercise, according to a UAB study.