Research & Innovation
The research team analyzed the clinical outcomes of more than 12,000 patients who had a TEE-guided percutaneous transcatheter intervention and found that, over the past decade, 3.6 percent of patients who had this procedure had complications.
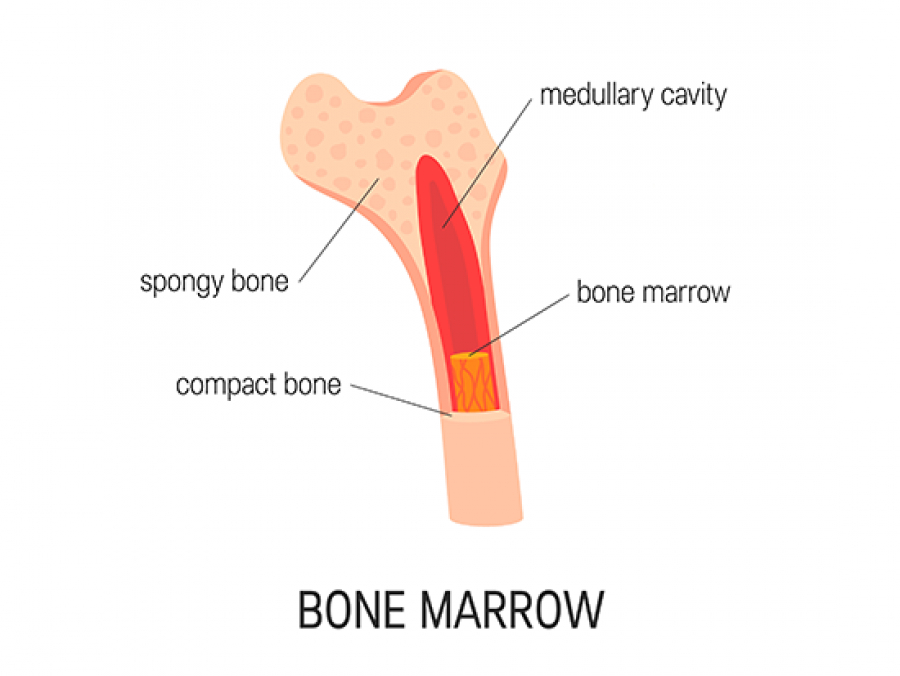
An overabundance of mast cells, which are important components of the immune system and are produced in the bone marrow, can lead to a variety of health issues.
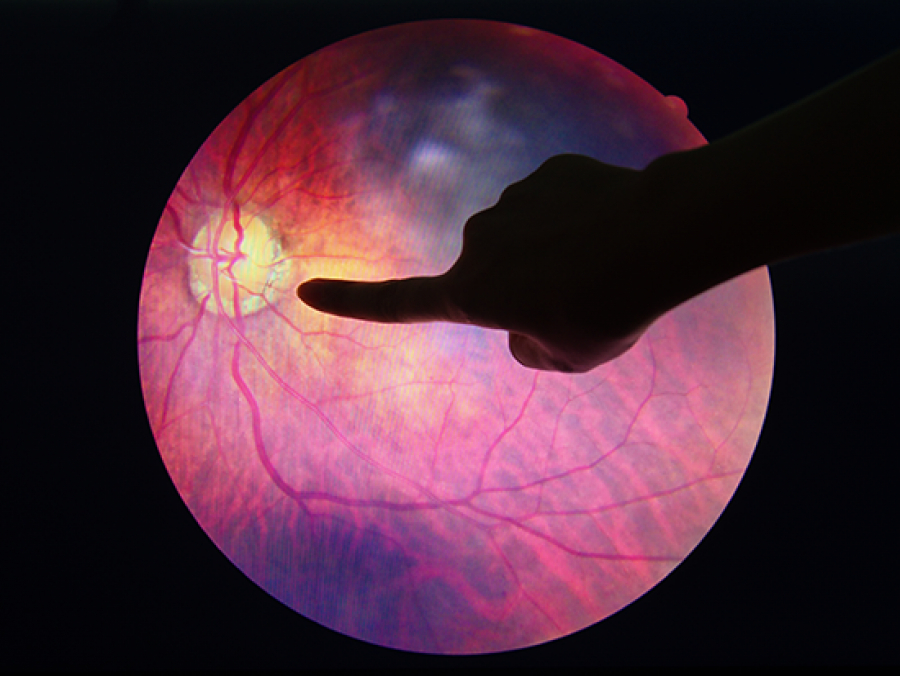
Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in American adults. The source of this damage may lie in the belly — mainly a leaky small intestine. A novel treatment can possibly prevent or reverse this damage.
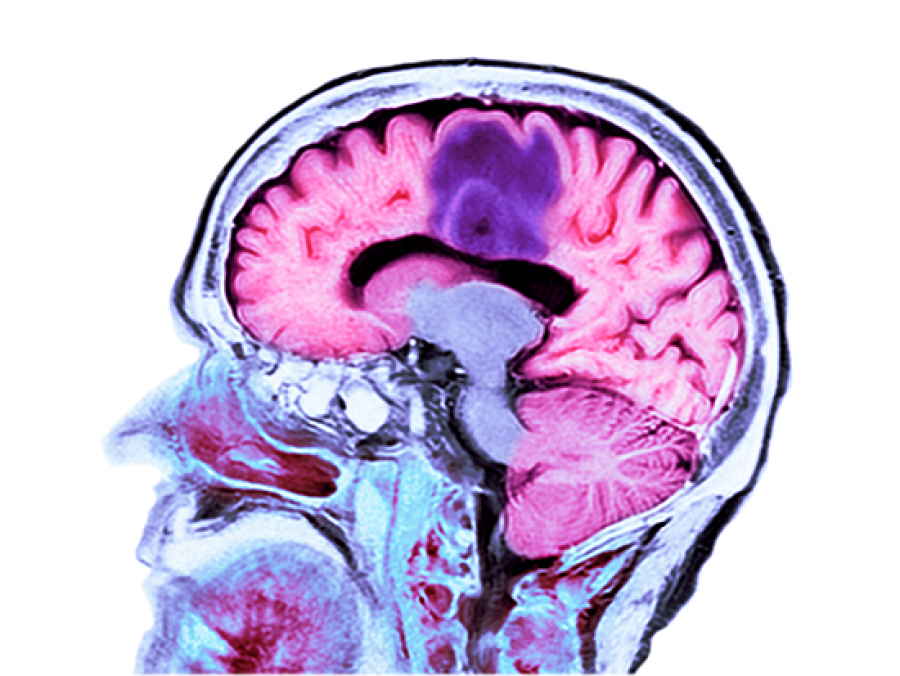
The spinoff company, IN8bio Inc., uses proprietary drug-resistant immunotherapy licensed in part from UAB. Glioblastoma is the most aggressive type of cancer originating in the brain.
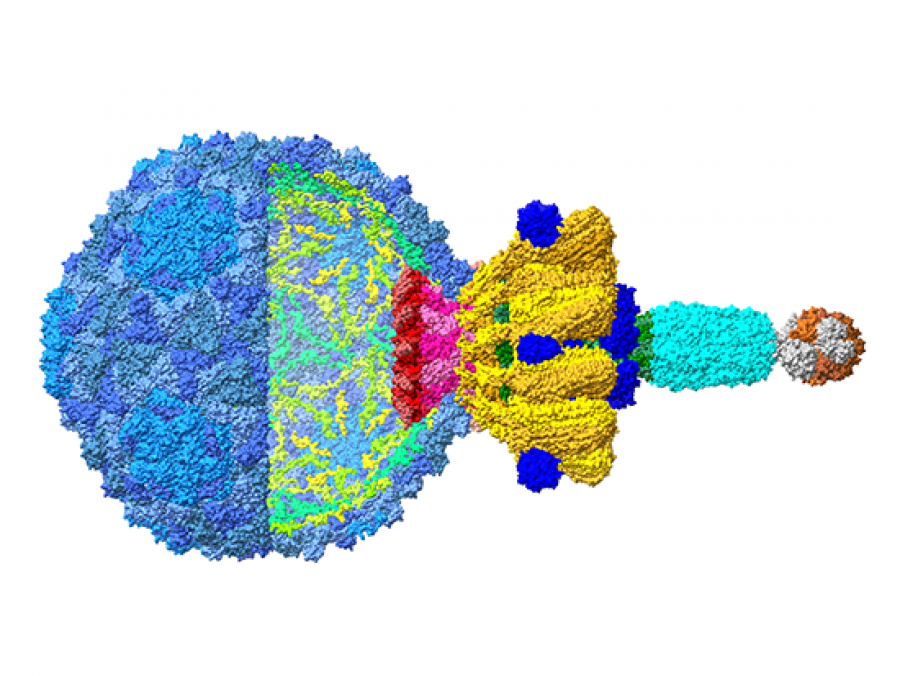
High-resolution knowledge of structure is a key link between viral biology and potential therapeutic use of the virus to quell bacterial infections.
The funding will support 24 research projects at seven institutions in Alabama.
The study, utilizing the relatively new field of metagenomics, demonstrated an imbalance in the gut microbiome of patients with Parkinson’s disease.
UAB researchers have published an article demonstrating how the term “aggressive care,” used loosely by clinicians to describe care that can negatively impact quality of life for patients with serious illness, is often used to inappropriately label the preferences of African American patients.
The gift will advance the use of induced pluripotent stem cells as a potential therapy for Alzheimer’s disease.
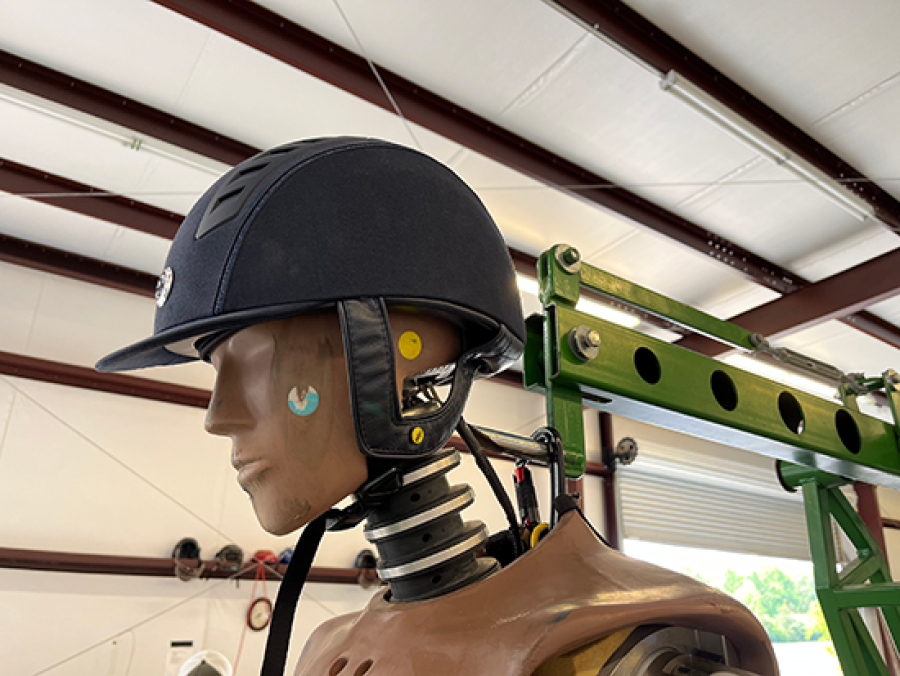
Gould’s helmet research added variables such as fall height and the type of surface struck.
Given the rising rates of obesity and diabetes, semaglutide could be used effectively to reduce the burden of these chronic diseases.
The UAB Marnix E. Heersink School of Medicine leadership team outlined key research focus areas to ensure continued growth over the next five to seven years.
Knockout of TXNIP improves diabetes-associated hyperglycemia and hyperglucagonemia.
Published results suggest the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated the slow increase in pediatric Type 2 diabetes.
The clinically approved drug ruxolitinib suppressed a mouse model of melanoma that is resistant to immune checkpoint blockers.
The UAB projects will investigate was to improve and increase the use of artificial intelligence in biomedical research.
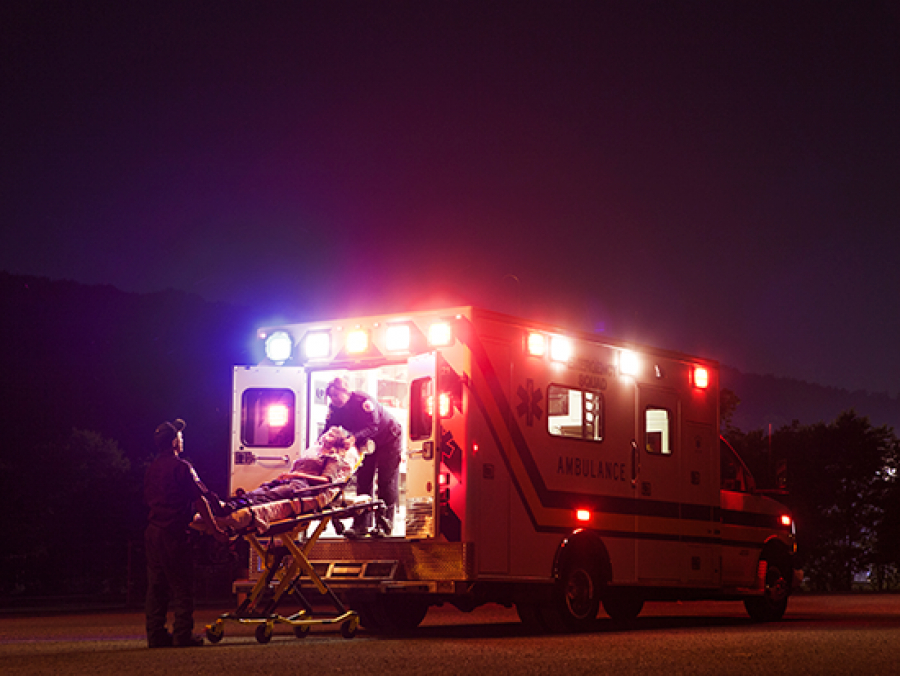
The study, an exception from informed consent trial, will compare whole blood to blood components in the treatment of traumatic injuries.
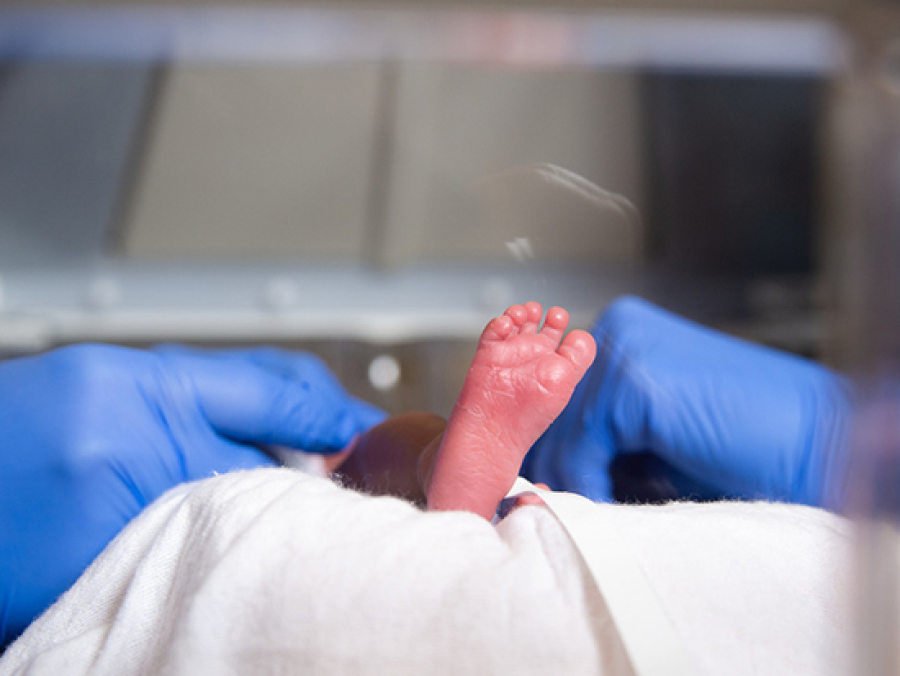
Noninvasive ventilation is possible in infants at limits of viability. But unlike in slightly older preterm infants, noninvasive ventilation did not show an advantage in infants of 22 weeks-0 days to 23 weeks-6 days gestational age.
Social media has been a useful tool to inform a community about research studies that are exempt from informed consent protocols.
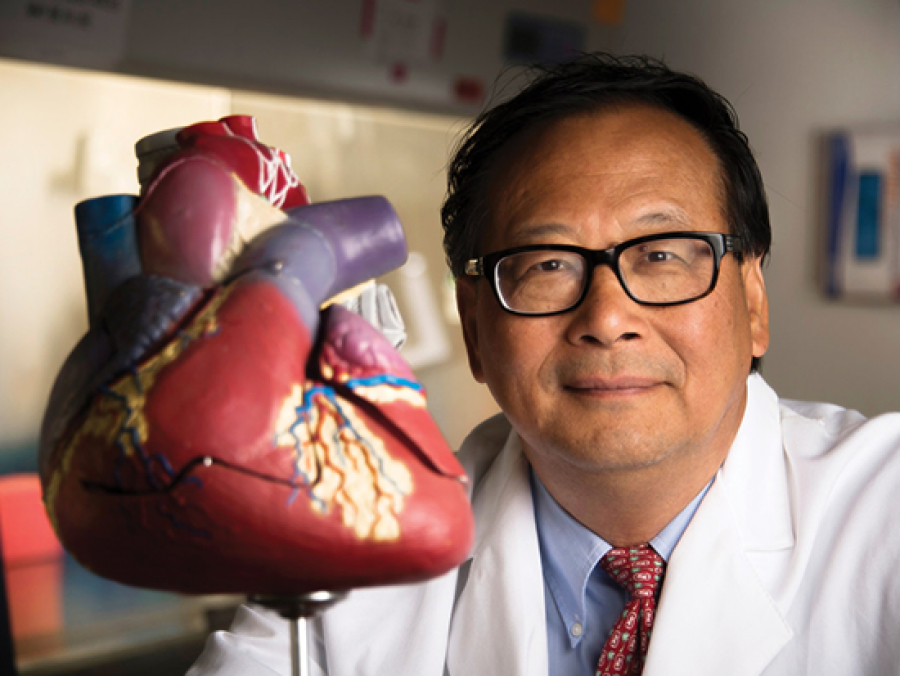
Zhang wins $11.2 million NIH PPG grant to improve heart attack recovery through growth of new heart muscle cells.
The deciphering of a new signaling cascade sheds light on how mutations in metabolism cause normal cells to become cancerous.
Results published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease show patients with one cancer diagnosis were less likely to develop dementia and had an overall slower cognitive decline than patients with no history of cancer.
A novel activity against hypothiocyanite has been found for an E. coli enzyme and homologs enzymes in Streptococcus, Staphylococcus and Bacteroides species, with implications for diseases like cystic fibrosis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Emergency department workers were the first line of defense against COVID, but their risk of infection was higher when they were not at work in their hospitals.
The researchers found that ARID1A-deficient bladder cancers are sensitive to combination therapies with the EZH2 inhibitor and inhibitors of PI3K, in a synergistic manner.
Women who have never smoked have smaller lung airways than men do, leading to higher risk for COPD.
The first known U.S. study evaluates the mental health of practicing dentists and dental hygienists during the COVID-19 pandemic.
X-ray crystallography revealed the structure of the HIV-1 matrix protein at 2.1 angstroms resolution, advancing understanding of key mechanisms of viral assembly.
Surprisingly, several competing models for this clathrin-mediated endocytosis all appear to function in two cell lines tested.
The investigators will look at diet’s impact on mobility, physical and cognitive function, as well as on pain, fatigue, sleep, mood and anxiety, in people with multiple sclerosis